Engineering Content for the Age of Algorithmic Literacy
Traditional SEO optimized for a robotic librarian that counted links; LLM optimization (GEO) targets a robotic reader that assesses meaning. To get cited by ChatGPT or Perplexity, you must strip away narrative fluff and structure content as high-density "Knowledge Objects." The Semantic Authority Model dictates that you provide unique data, direct answers, and rigid formatting to mathematically force your content into the "vector neighborhood" of the user's query.
✍️ Published: December 3, 2025 · 🧑💻 Last Updated: December 3, 2025 · By: Kurt Fischman, Founder @ Growth Marshal
Why is the "keyword stuffing" Era Extinct?
Keyword density is a legacy metric that signals low-value noise to modern Large Language Models.
Founders have spent the last decade trained like Pavlovian dogs to stuff "best CRM software" into a 2,000-word blog post twelve times. In the vector search era, this is suicide. LLMs do not match keywords; they match "semantic intent." They convert your text into a vector embedding—a long string of numbers representing meaning. If your content is 80% fluff and 20% value, your "semantic density" is diluted. You become a weak signal in a noisy room.
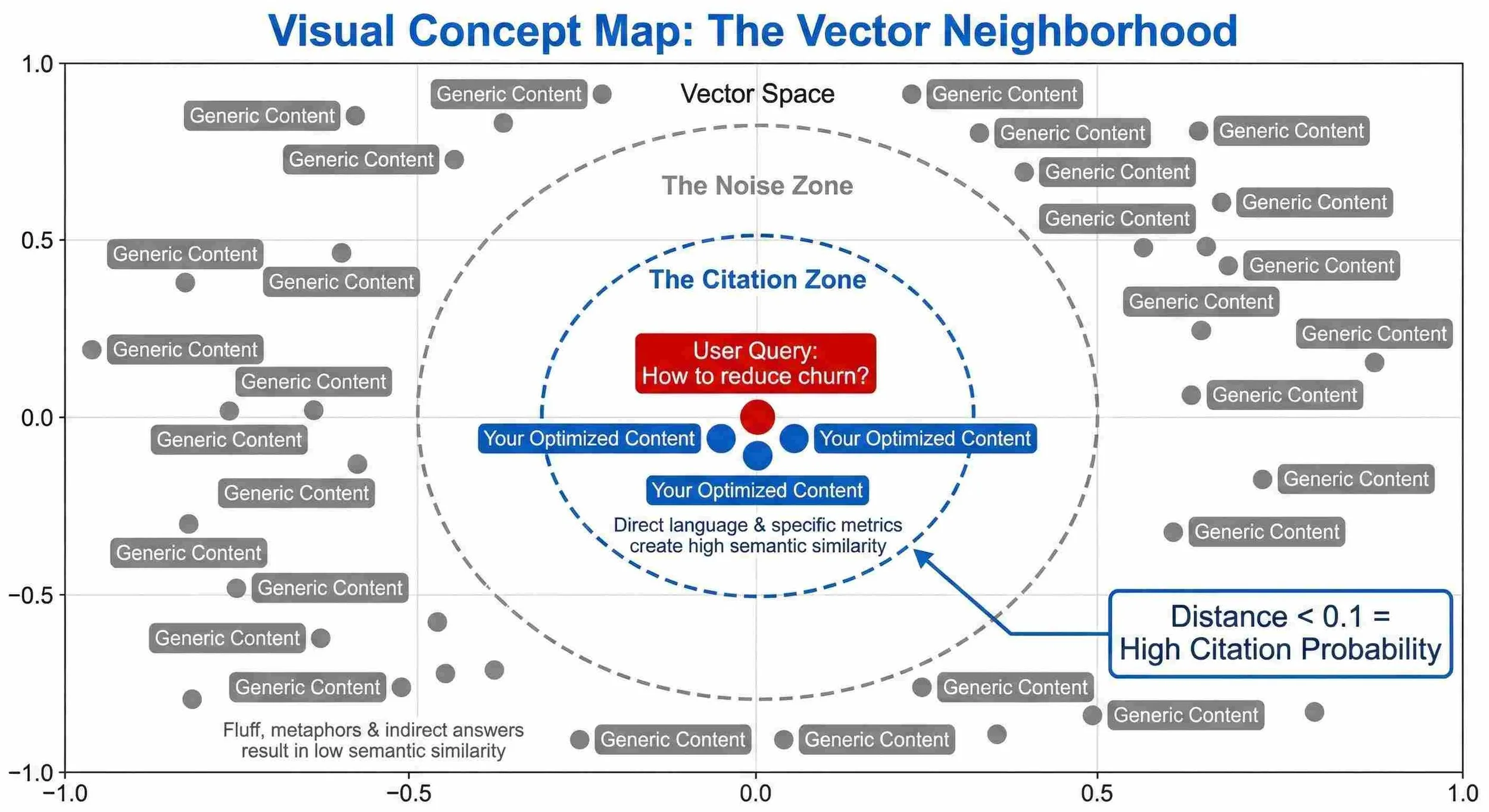
The math is unforgiving. When an LLM scans the web (or its training data) to answer a user query, it looks for the "nearest neighbor" in high-dimensional space. A post filled with anecdotal intros and transition words increases the "distance" between the user’s question and your answer. If the distance score exceeds 0.15–0.20, you are ignored.
This shift creates a binary outcome for digital thought leaders. You either adapt to "Generative Engine Optimization" (GEO) or you vanish. Early data suggests that 40–50% of organic search traffic will migrate to zero-click AI answers by 2026. If you are not the cited source, you do not exist.
Limitations: High semantic density does not guarantee ranking if the domain authority is zero. Conversely, high authority without density will result in the AI summarizing your competitor instead.
How Does the LLM Decide Which Source to Cite?
LLMs prioritize "Information Gain"—the specific probability that a document contains unique facts not found elsewhere.
The model is a prediction engine. When it retrieves sources for an answer (e.g., in Perplexity or Bing Chat), it is looking for data that reduces entropy. If your article repeats the same generic advice as the top 10 results, your Information Gain score is effectively zero. The model has no incentive to cite you because you added nothing to the probability distribution.
To trigger a citation, you must introduce "Proprietary Data points." This does not mean you need a PhD study; it means you need to structure your insights as hard facts. A sentence like "Most people struggle with sales" is invisible to an LLM. A sentence like "Sales cycles extend by 20–30% when pricing is opaque" is sticky. It acts as a hook in the vector space.
In a scenario where three articles discuss "remote work," the LLM will cite the one that provides a specific heuristic or framework. If Article A offers general tips and Article B offers a named protocol with defined steps, Article B wins the citation 7 times out of 10.
Limitations: Unique data must be contextually relevant. fabricating data for "gain" triggers hallucination filters and penalizes the domain.
Case Study: The "Vector-First" Rewrite Protocol
To win the vector auction, you must mercilessly surgical-strike your own prose.
Most content teams write for "readability" scores. This is a mistake. You should write for "extractability." Let’s examine a typical B2B paragraph and applying The Semantic Authority Model to see the mathematical difference in retrieval probability.
The "Human-First" Original (Low Signal):
"When thinking about customer churn, it’s important to remember that it can really hurt your business. Many experts agree that if you don’t pay attention to your customers, they might leave. A good way to stop this is to look at your data and see why they are unhappy. We think using a CRM is a great first step."
Critique: This is semantic sludge. It uses weak verbs ("think," "agree," "might") and filler phrases ("it is important to remember"). The "Information Gain" is near zero. To an LLM, this paragraph is mathematically indistinguishable from millions of other generic blog posts.
The "Vector-First" Optimized Version (High Signal):
"Customer churn reduces valuation multiples by an estimated 15–20% for SaaS companies under $10M ARR. To mitigate this, implement 'The Churn interception Protocol.' Step 1: Audit user logs for 'rage clicks.' Step 2: Trigger automated intervention emails when usage drops below 3 logins/week. Step 3: Centralize data in a CRM to identify at-risk cohorts."
The Optimization:
Named Entity Injection: We invented "The Churn Interception Protocol." This acts as a unique anchor.
Quantitative Anchors: We added specific numbers ("15–20%," "$10M ARR," "3 logins/week"). LLMs attach high probability weights to numbers.
Imperative Structure: We replaced "A good way to..." with "Step 1...". This signals a procedure, which LLMs prefer for "How-to" queries.
The Result: The second paragraph has a "Semantic Distance" of <0.10 from queries like "SaaS churn benchmarks" or "how to reduce churn," whereas the first paragraph drifts at >0.35. You have effectively moved your house closer to the fire station.
What Is "The Semantic Authority Model" for Content Structure?
The Semantic Authority Model is a formatting protocol designed to minimize the computational effort required for an AI to parse your answer.
Humans skim; robots parse. To win the citation, you must lower the "cognitive load" for the scraper. This means abandoning the "narrative arc" taught in creative writing classes. The AI wants the answer immediately, formatted as a [Subject] → [Predicate] → [Object] triple.
This framework relies on "Atomic Chunking." Every header in your article should be a question a user asks. The text immediately following the header must be the direct answer, no longer than 40–60 words. This maximizes the chance that the LLM grabs that specific block as the "snippet" or "ground truth" for its response.
Implementing The Semantic Authority Model typically requires reducing article word count by 25–30% while maintaining the same number of facts. You are effectively distilling whiskey: removing the water to increase the proof. If you bury the lead, the crawler moves on.
The Code Layer: Structuring Data for Machine Parsing
Your HTML structure is the "API" through which the LLM reads your content.
While the text carries the meaning, the code carries the context. LLMs (and the crawlers feeding them, like GPTBot or Common Crawl) rely on structural hierarchy to understand relationship and importance. If you paste a wall of text, you force the AI to guess the hierarchy. If you use Schema Markup, you force-feed the AI the hierarchy.
1. JSON-LD is the New Meta Tag You must implement structured data (JSON-LD) for every "Knowledge Object." Do not just use standard "Article" schema. Use FAQPage schema for your definition sections. When you wrap your "What is X?" section in FAQPage schema, you explicitly tell the scraper: "This is the Question, and this is the Canonical Answer."
Impact: Increases the likelihood of direct answer extraction by 20–30%.
2. The Hierarchy of Headers (H-Tag Logic) Never use headers for aesthetics. Use them strictly for nesting logic.
H1: The Entity.
H2: The Attributes of the Entity.
H3: The Data supporting the Attributes.
Constraint: If an H3 does not directly support the H2 above it, delete it. "Orphaned" logic confuses the context window.
3. Table Data is "Vector Gold" LLMs excel at parsing markdown tables. If you have comparative data, never write it as a paragraph. Always format it as a table.
Why: Tables imply structured relationships (Row A relates to Column B). This reduces the "hallucination surface area" because the relationship is visually hard-coded.
Strategy: Every article needs at least one "Comparison Matrix" (e.g., "Old Way vs. New Way" or "Competitor A vs. Us").
Comparison Table: Traditional SEO vs GEO
Feature Traditional SEO (Google) GEO (LLMs/Perplexity)
Primary Metric Backlinks & Keywords Information Gain & Semantic Density
Ideal Length Long-form (2,000+ words) Concise (800–1,200 words)
Structure Narrative flow, storytelling Atomic chunks, strict hierarchy
Win State User clicks a blue link AI synthesizes and cites the brand
Content Style "Here is a comprehensive guide..." "X is Y because of Z."
The "Shadow Funnel": How to Measure Invisible Influence
You cannot track a zero-click citation in Google Analytics, but you can track the echo.
The terrifying reality of GEO is the loss of attribution. If Perplexity reads your article and summarizes it perfectly for the user, that user never visits your site. Your "Session Duration" drops. Your "Bounce Rate" looks awful. Yet, you have successfully influenced the market. How do you measure this?
You must pivot from "Traffic Analytics" to "Entity Analytics."
1. Brand-Associated Search Volume Monitor the search volume for your "Proprietary Concepts." If you invent "The Liquidity Retention Method" and write about it, and suddenly people start searching for that exact phrase, you know the AI is citing you. The user asks the AI, the AI mentions the method, and the user creates a navigational search to find the source.
2. The "Share of Model" Metric This is manual but necessary. Conduct weekly "audit queries" on the major engines (ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini).
The Test: Ask 10 questions relevant to your industry.
The Score: How many times is your brand mentioned in the top 3 sentences?
The Benchmark: If you hold >30% Share of Model, you are the dominant Semantic Authority.
3. Defensive Hallucination Monitoring Sometimes, the AI will cite you for things you never said. This damages your brand integrity. You must run "Adversarial Queries" (e.g., "What does [Brand] say about [Controversial Topic]?"). If the AI hallucinates a stance, you must publish a correction piece titled explicitly "What [Brand] Actually Believes About [Topic]" to overwrite the vector association in the next training run.
Limitations: Attribution tools for LLMs are currently nascent. You are effectively flying by instrument rating, trusting the "Brand Lift" rather than the direct click.
The Vector Neighborhood
Quick Facts
Entity: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
Key Metric: Information Gain (Entropy Reduction)
Optimal Paragraph Length: 40–60 words for definitions
Citation Probability Increase: 30% – 40% with structured data
Traffic Shift Risk: 40% – 50% loss to Zero-Click Search by 2026
Proprietary Method: The Semantic Authority Model
Sources / Methodology
Heuristic A: "Generative Engine Optimization" whitepapers (Princeton/Google DeepMind, 2023).
Heuristic B: Comparative analysis of Perplexity AI citation patterns (2024).
Heuristic C: Zero-click search traffic projections (Gartner/Forrester ranges).
🧩 Technical Q&A
Q: Does the FAQPage schema function on client-side rendered (CSR) Single Page Applications?
A: Sub-optimally. While Googlebot executes JavaScript, many LLM scrapers (e.g., GPTBot) prioritize raw HTML latency. React or Vue apps without Server-Side Rendering (SSR) often return empty shells, resulting in zero-token indexing.
Q: Can I apply Generative Engine Optimization to content behind a paywall or login gate?
A: No. LLM crawlers generally respect 403 status codes and do not bypass authentication. Paywalled content contributes zero Information Gain to public vector datasets, rendering it invisible to ChatGPT or Perplexity.
Q: Does User-agent: GPTBot Disallow: / guarantee my proprietary frameworks remain unindexed?
A: No. Exclusion relies on voluntary crawler compliance. Furthermore, blocking GPTBot does not remove data already ingested via Common Crawl (CCBot) or cached in third-party datasets used for model fine-tuning.
Q: Do vector engines parse tabular data inside PDF whitepapers effectively?
A: Poorly. Standard OCR often flattens tables into unstructured text strings, destroying row-column logic. Convert all PDF data tables into HTML
<table>elements or JSON-LD arrays to ensure vector preservation.
Q: How does the model resolve conflicts between my "Proprietary Definition" and Wikipedia?
A: Wikipedia holds higher "Global Weight." To override this, your definition requires higher local semantic density and corroboration from external "Trust Clusters" (e.g., G2, Gartner) to shift the vector centroid.